
The Early Feeding Skills (EFS) Assessment is a clinical tool designed to evaluate infants’ feeding readiness and abilities. It provides a structured approach to assess development in preterm and at-risk infants in relation to feeding.
Dive into the world of pediatric care, and you’ll often encounter the Early Feeding Skills Assessment (EFS) PDF, a document keenly sought after by healthcare professionals specializing in neonatal and infant care. This assessment tool is pivotal in determining the development of feeding skills in infants, particularly those born prematurely or with medical conditions affecting their ability to feed.
The EFS Assessment aids in creating personalized feeding plans to support infants’ growth and nutritional needs efficiently and effectively. By evaluating critical factors such as engagement, oral-motor function, and coordination of swallowing and breathing, the EFS guides clinicians in identifying areas where an infant might need additional support or intervention.
Credit: www.nature.com
Assessing early feeding skills is crucial for infants’ health and development. This process involves various methods that health professionals use to ensure a child’s feeding capabilities are progressing well. Today, we delve into the nuanced approaches of Early Feeding Skills Assessment, providing invaluable insights into a child’s oral-motor development and feeding efficiency.
Professionals begin by observing an infant’s ability to manage food using their mouth, lips, tongue, and jaw. They look for movement coordination, strength, and endurance in these areas. Some key points include:
Synchronized actions between sucking, swallowing, and breathing are essential for safe feeding. Professionals assess this coordination through careful monitoring:
Spotting early signs of feeding difficulties can prevent future complications. Red flags assessed may include:
| Signs | Potential Issues |
|---|---|
| Gagging or coughing | Swallowing disorders |
| Extended feeding times | Inefficient sucking |
| Poor weight gain | Inadequate nutritional intake |

Credit: www.thelancet.com
Understanding the Early Feeding Skills Assessment (EFSA) is key to ensuring healthy growth in infants. This tool is instrumental in pinpointing potential feeding problems and aligning them with appropriate interventions. However, while it holds remarkable benefits, professionals must also acknowledge the inherent challenges it poses.
Early detection of feeding difficulties can prevent future complications. The EFSA helps in identifying issues that could undermine an infant’s nutrition and growth. Timely interventions based on the assessment can significantly improve a child’s overall development. Challenges include ensuring accurate assessment and having qualified professionals to interpret the results and recommend interventions.
The primary goal of an EFSA is to enhance infant nutrition. By recognizing and addressing feeding difficulties early on, the risk of malnutrition decreases, promoting optimal growth and development. Challenges here stem from the diverse nature of feeding issues and the individualized care required for each infant.
While the EFSA is a powerful tool, it is not without constraints. One potential limitation is the need for professional expertise in administering and interpreting the assessment. In regions lacking trained professionals, this could limit the utility of such assessments. Additional considerations include the adaptability of the assessment tool to various cultural and dietary factors, which could affect its effectiveness in diverse settings.
Credit: www.nature.com
The Early Feeding Skill Assessment is a checklist to evaluate an infant’s readiness and capabilities during feeding.
To assess baby feeding, monitor their latch, sucking rhythm, and swallowing patterns. Note their alertness, comfort level, and satiety cues after feeding.
Yes, the Early Feeding Skills (EFS) Assessment and cue-based feeding scales are considered valid and reliable for assessing preterm infants’ oral feeding skills.
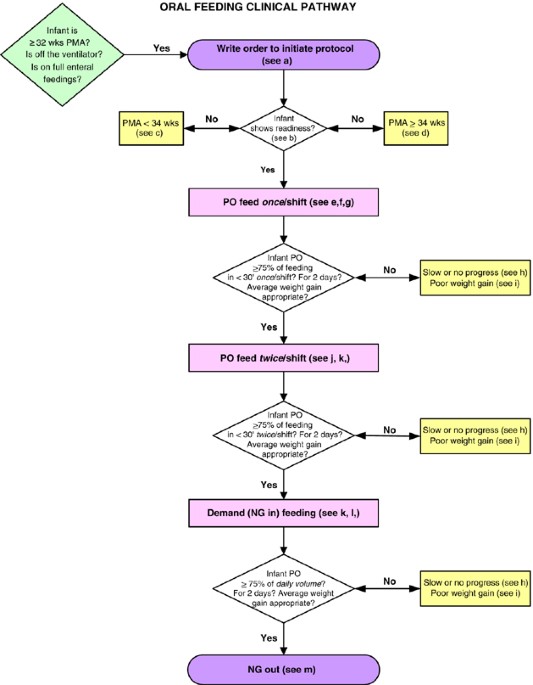
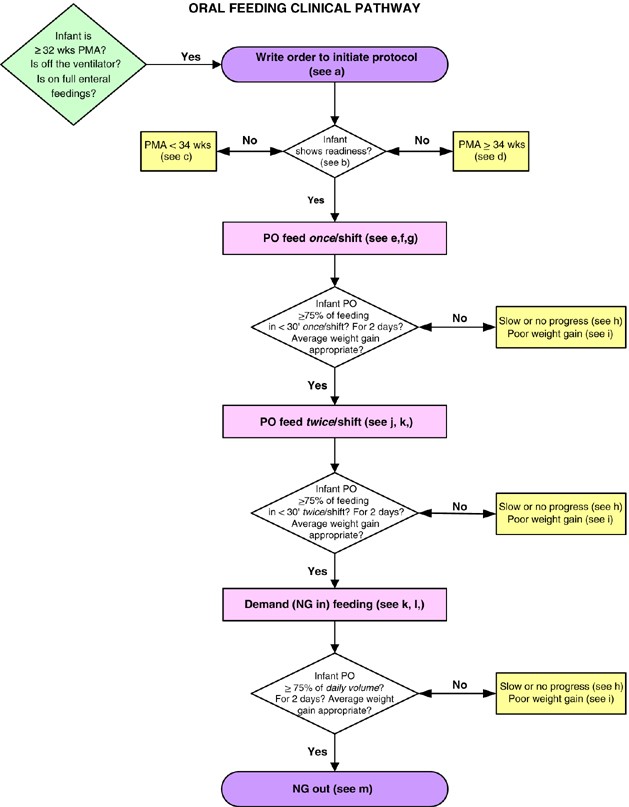
The NICU feeding protocol typically includes: assessing infant readiness, using a gradual progression of feed volumes, monitoring tolerance, adjusting based on individual needs, and promoting maternal breast milk when possible.
As we wrap up this discussion on the importance of early feeding skills assessment, remember that the right tools offer invaluable insights. They guide healthcare providers in supporting infants’ nutritional journeys, ensuring safe and effective feeding practices. The Early Feeding Skills Assessment PDF serves as a key resource, enabling a structured approach to track and enhance feedings in early life.
Empower your practice with this knowledge, fostering healthy growth from the start.